Certification of Documents, Emails, Agreements, etc.¶
In this use case we will show how to add transparency to a particular
transaction or agreement that got captured in a DOCUMENT, by
allowing the issuer to certify that the document has not been altered.
Theory and Operation¶
Tip
For the sake of clarity, Document is anything that could be suitable to keep track of the original transaction, such as Emails, Agreements, Dues, etc…
First of all, we need to identify what are the elements of the problem to address and how we can adapt them to the components defined in our QED’s trust model: information, actors and mapping function(s).
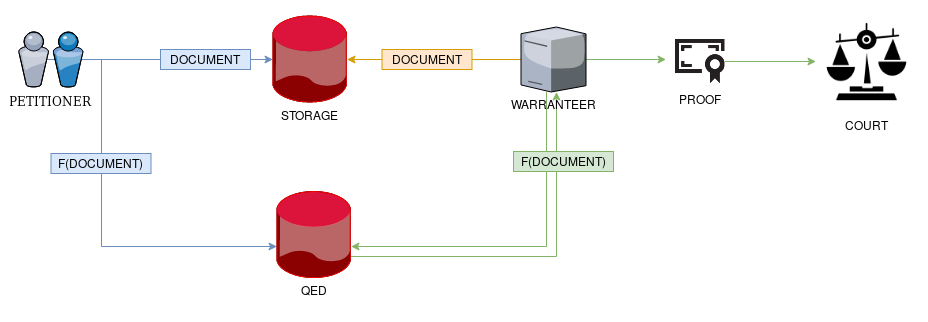
As we can see from the figure, the information we want to add transparency to,
is the DOCUMENT itself, which gets inserted in a particular
STORAGE. This storage acts as the information provider, and it can be
considered as untrusted.
The PETITIONER is the actor interested in keeping track of the contents
of the document, so he takes the role of source of information and
inserts the document into the storage.
Simultaneously, he uses a mapping function F to translate the
information to a unique QED event F(DOCUMENT). He could use the
SHA256 digest of the contents of the document.
Note
F output example:
{
"digest": "4b1a0b7be7b5982dc778e76adacbb6348632ff4d",
}
Now, suppose there is a court trial that demands proofs of integrity
to the entity in charge of keeping the document, the one we have
called WARRANTEER. This actor also have to act as the
information consumer in the trust model, and thus, needs to
have confidence in the integrity of the storage.
To do that, it could use the same mapping function F to generate
again the QED event and then, ask for a membership proof to the QED Log.
Combining the resulting cryptographic proofs with the QED
event, the WARRANTEER could verify the original information as valid.
Working example¶
Warning
The following snippets assume a working QED installation. Please refer to the Quick start page.
The following snippet simulates the creation of a QED event starting from
the DOCUMENT recently emitted. As mentioned before, we are using the
SHA256 digest of the contents of the file as the output of the mapping
function F1(DOCUMENT) to unambiguously identify the document.
# Create the document event
document_hash=$(sha256sum <document> | cut -d' ' -f1 )
cat > document_event.json <<EOF
{
"document_hash": "${document_hash}",
}
EOF
Alongside inserting the document into the storage, we add the event to the QED Log.
# pushing the document event to QED server
qed_client \
add \
--event "$(cat document_event.json)"
Finally, we can generate again the QED event to request a membership proof from QED Log and verify the proof.
# Verify the proof
qed_client \
membership \
--event "$(cat document_event.json)" \
--auto-verify